Have you ever wondered why some animals look a bit different? It could be due to mutations. Imagine spotting a bird with bright, unusual feathers in your backyard. Isn’t that fascinating? These unique traits might be changes in their genes. But which mutations are easiest to ID visually?
While some changes are hard to see, others are clear as day. Take, for example, fruit with strange colors or flowers with extra petals. These differences grab our attention right away. Have you seen an apple that’s oddly shaped? That’s a clue from nature!
Kids often ask, “Why does that cat have extra toes?” Such changes are called mutations. They happen when living things grow or change. So, next time you see something that looks curious in nature, remember: it might be one of those easy-to-spot mutations. Keep your eyes open, and you never know what surprises you’ll find!

Identifying Visual Mutations: A Guide To Easy Detection
Which Mutations Are Easiest to ID Visually?
Some mutations jump out like red spots on a giraffe. Eye colors, like blue or green, often grab attention. Ever seen a cat with extra toes? That’s an easy mutation to spot. Albinos, with their pale skin and hair, are rare but noticeable. Some plant mutations, like a sunflower with more petals, also stand out. Can you spy these changes in your backyard? It’s like nature’s treasure hunt!
Understanding Genetic Mutations
Definition of genetic mutations. Types of mutations: Point mutations, insertions, deletions, and more.
Genetic mutations are changes in DNA. They can happen naturally or due to environmental factors. There are various types:
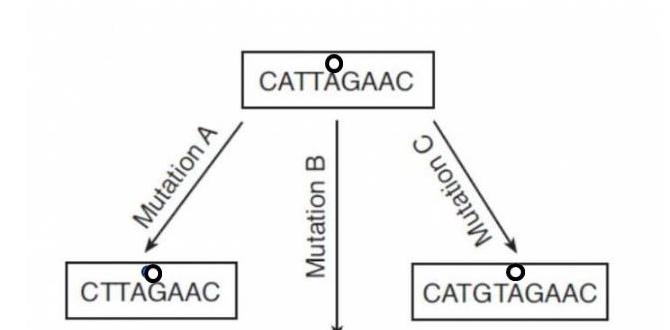
- Point Mutations: These change a single DNA letter. Think about it like changing a word in a sentence.
- Insertions: Extra DNA letters are added.
- Deletions: Some DNA letters are missing.
- More: Sometimes, entire sections of DNA are affected.
Each mutation affects how genes work. They can lead to visible traits or health changes.
Which mutations are easiest to identify visually?
Color changes in plants and animals are easy to see. Albino animals, with white skin, are a good example.
Visual Indicators in Phenotypic Mutations
Explanation of phenotypic mutations. Common visual traits resulting from mutations.
Phenotypic mutations show up in how organisms look. These changes happen in the genes and can be seen with your eyes. Some visual signs of mutations are easy to notice. For example, changes in the color of eyes, size, or shape of a body part are common. Sometimes animals can have fun marks or colors that stand out.
- **Size Change:** Altered growth in plants or animals.
- **Color Variation:** Bright colors or unusual patterns.
- **Shape Change:** Different forms or structures.
What are the most visible genetic mutations?
Color and size changes are easy to spot in nature. Many people notice plant leaf colors and animal fur patterns. Another is body part shape. This can happen in plants with differently shaped leaves. Many times, people see it right away.
Is it not cool how mutations work? They help species adapt and survive. Some scientists say, “Nature is the best artist.” Did you know that many flowers have mutations that help them attract bugs for pollination? This is how nature uses changes to keep life going! Understanding these visible mutations makes nature more fascinating for everyone.
Color Mutations: The Most Visible Indicators
Examples of mutations causing color changes in animals and plants. Case studies: Albino animals, melanism, and plant variegation.
Color changes in animals and plants can be quite amazing. Some animals are born albino. This means they don’t have any color. The opposite of albino is melanism, where animals have extra black or dark colors. Plants can show color changes too. This is called variegation. It’s like having multicolored leaves, which look like nature’s painting.
What is albino mutation?
An albino mutation occurs when an animal lacks pigment, resulting in white skin or fur and pink eyes.
- Albino Animal Example: Albino snakes, which miss color in scales.
How does melanism affect animals?
Melanism causes more dark pigment, turning animals black or very dark.
- Melanism Example: Black panthers.
What is plant variegation?
Plant variegation is when leaves have two or more colors. This happens because of genetic changes.
- Plant Variegation Example: Holly leaves with green and white patterns.
These mutations make spotting them easy. Nature’s way of mixing colors is indeed fascinating!
Structural Mutations and Their Visual Traits
Description of structural mutations affecting appearance. Notable examples: Polydactyly, dwarfism, and gigantism.
Some mutations change how creatures look, and aren’t they fascinating? Imagine spotting an extra toe or super tiny or huge animals! These are called structural mutations. They often give noticeable traits, making them easy to spot. For instance, polydactyly means having extra fingers or toes. It’s like getting a free finger for every purchase! Meanwhile, dwarfism produces tiny, adorable animals, and gigantism results in giant beings. Now, isn’t that a sight!
With such striking appearances, these traits are like Hollywood celebrities—hard to miss!
| Mutation | Visual Trait | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Polydactyly | Extra digits | Cats with extra toes |
| Dwarfism | Short stature | Dwarf ponies |
| Gigantism | Large size | Elephants |
Patterns and Textures as Mutational Signs
Impact of mutations on patterns and textures in organisms. Examples: Striped, spotted, and marbled organisms.
Mutations can create unique patterns and textures in living things. Think of a zebra’s stripes, a leopard’s spots, or a marble frog. These eye-catching designs show how mutations affect nature. Imagine giraffes with polka dots, leading to fashion trends in zoos! Scientists study these mutations with excitement, spotting changes easily with their own eyes. Below is a fun chart to see how some patterns play out in the wild:
| Animal | Pattern |
|---|---|
| Zebra | Stripes |
| Leopard | Spots |
| Marbled Frog | Marbled |
Challenges and Limitations in Visual Identification
Explaining difficulties in relying solely on visual clues. Importance of genetic testing for confirmation.
Spotting mutations with only your eyes can be tough. Some changes are hidden, like those inside cells. Even if you spot something, it might not tell the whole story. This is why genetic testing is key. It offers a clearer picture. Our eyes can’t catch everything, like subtle traits or ones that blend in with others. Reliable science tools can help. Did you know, many organisms only show hints of big changes? It proves that seeing isn’t always believing, and tests back up what we might see.
Which mutations are easiest to identify visually?
Visible mutations can include color changes and size differences. Birds with different feather colors or flowers with extra petals are often easy to spot. But even with clear signs, a specific test might still be helpful. For example:
- Albinism: Lack of pigment makes it easy to see.
- Polydactyly: Extra fingers or toes stand out.
- Dwarfism: Different body sizes are noticeable.
Did you know? Around 90% of mutations need genetic tests to be confirmed, even if they look obvious!
Importance of Identifying Visual Mutations
Role in biodiversity and evolutionary studies. Implications for conservation and breeding programs.
Finding visual changes in animals matters a lot. It helps scientists learn about life and how it changes. Some changes you can see with your eyes tell stories of past lives. These changes also help care for animals and make sure they live well in the future. Visual changes, like bright colors or unusual patterns, are signs and clues. They help in preserving animals and in choosing which animals to raise. This makes nature rich in life.
What are some examples of visual mutations?
Some animals show visual mutations. These are easy to spot. For example, albino animals have no color in their skin, hair, or eyes. Peacocks sometimes have all-white feathers. Other birds might have unique spots or stripes. These changes are often due to a single change in their genes.
How do visual mutations help in conservation?
Visual mutations help track animal numbers. By spotting these changes, scientists can count and study animals better. It helps in knowing if an animal group is in danger. This way, steps can be taken to protect them.
Why are visual mutations important in breeding?
In breeding, knowing which traits are passed on is crucial. Visual mutations are easy to identify and can show which animals carry special genes. This helps breeders select animals with desired traits for future generations. It ensures the health and variety of animal groups.
Some key points of visual mutation benefits:
- Easy identification helps in animal tracking.
- Keeps biodiversity by maintaining genetic variety.
- Ensures healthier future animal populations.
A wise saying goes, “Variety is the spice of life.” This holds true in nature. With each unique trait, life gains color, strength, and resilience.
Future Prospects in Visual Mutation Identification
Advances in technology enhancing identification accuracy. The potential impact on research and biodiversity conservation.
Technology helps us see mutations better. Now, we can use cool gadgets to look closer at tiny details. Powerful microscopes and AI tools help scientists spot changes in creatures easily. This helps study nature and save animals. With these advances, researchers can understand biodiversity better. This can help conserve different species around the world.
Which mutations are easiest to ID visually?
Some mutations are easy to see. Color changes in animals are one example. These changes can often be viewed with our eyes alone. Things like albino animals or different patterned plants are noticeable. These changes do not need special tools. You can see them with a clear view.
Conclusion
Identifying mutations visually is easier when changes are big and obvious, like color or shape differences. You’ve learned that noticeable features make it simpler. Keep exploring the fascinating world of genetics to discover more. Encourage others to be curious too, and maybe someday, you’ll help uncover new ways to spot these amazing mutations!
FAQs
Certainly! Here Are Five Questions Related To Identifying Mutations Visually:
Mutations are changes in DNA. Imagine DNA like a puzzle. If one piece changes shape or color, that’s a mutation. Sometimes scientists look at pictures of DNA to see these changes. By spotting differences, they can figure out what makes some animals unique or why some people get sick.
Sure! Let’s imagine someone asks why the sky is blue. You could say, “The sky looks blue because of the sun’s light. Light is made of many colors. When it hits the air, blue scatters everywhere. That’s why you see a blue sky!”
What Are Some Of The Most Common Visual Markers Or Physical Traits Used To Identify Genetic Mutations In Organisms?
Genetic mutations can change how an organism looks. Sometimes, you might see differences in fur or skin color, like a cat having a spot that’s a different color from the rest of its fur. Other times, you can spot changes in the size or shape of body parts, such as a plant having extra-large leaves. Animals or plants might also be smaller or larger than usual because of a mutation. These differences help us see that something special has happened in their genes.
How Can Pigmentation Changes In An Organism’S Appearance Signal Potential Genetic Mutations?
When an animal’s color changes, it might mean there’s a change in its DNA. DNA is like a recipe that tells our body what to look like. Sometimes, the “recipe” gets a bit mixed up, causing different colors. These color changes help scientists find where the mix-up happened. This helps them study and understand our bodies better.
Are There Specific Technological Tools Or Methods That Enhance The Visual Identification Of Mutations, Such As Uv Light Or Special Dyes?
Yes, there are special tools and methods to help us see changes, or mutations, in DNA. We can use UV light to make these changes glow, like a night light. Scientists also use colorful dyes to highlight these changes. These colors make it easier to spot mutations when looking through a microscope. This way, we can learn more about how living things change.
In What Ways Do Limb Deformities Or Structural Abnormalities Help Scientists Visually Identify Potential Genetic Mutations?
Limb deformities can act like clues for scientists. When they see unusual shapes or features, it can hint at genetic changes. By studying these changes, they learn about the genes behind them. It helps them understand human development and can lead to better treatments.
Can Eye Color Or Patterns In Animals Be Reliably Used As Indicators Of Genetic Mutations?
Yes, eye color and patterns can sometimes show genetic mutations. A genetic mutation is a change in an animal’s genes. These changes can make eyes a different color or give them unusual patterns. But not all eye oddities mean there is a mutation. Scientists use other methods to be sure.
Sure, I’d be happy to help! Please go ahead and share the question you’d like me to answer.
These Questions Can Help Guide An Exploration Of The Topic By Focusing On Different Aspects Of Visually Identifying Mutations.
When we look at changes in things like pictures, we call them mutations. To spot them, first, ask yourself how something looks different from before. Look closely at its shape, color, or size. Next, think about why it might have changed. Lastly, try to figure out if the change helps, hurts, or doesn’t affect it at all. This helps us understand how things grow and adapt.
